Your department just missed a critical deadline. Again. Issues are escalating to your desk that should have been resolved three levels down. Your CEO is asking why your corporate innovation initiatives aren’t delivering results while the digital transformation budget keeps growing.
Here’s the uncomfortable truth: Most companies hemorrhage money and talent not because they lack good ideas, but because they have no idea how their work actually gets done.
You can’t optimize what you can’t see. And right now, your most critical business processes are invisible—trapped in the heads of a few key people or buried in “that’s just how we’ve always done it.”
This is where corporate innovation through process mapping becomes your unfair advantage. Organizations that master this approach achieve:
- 50% reduction in cycle times without adding headcount
- 15-40% lower operational costs by eliminating hidden waste
- 30-50% productivity boost through systematic improvement
- 20:1 ROI on process optimization initiatives
Whether you’re a middle manager trying to bring order to organizational chaos, an operations leader tasked with “doing more with less,” or an executive who needs to demonstrate measurable improvements to the board, this guide shows you how to leverage process mapping for operational excellence.
Want to see how process mapping could transform your operations? Schedule a free consultation with Iterators to identify your biggest process bottlenecks and discover quick wins that could save you thousands in the first 90 days.
What Is Operational Excellence and Why It Matters in 2025
From Factory Floor to Digital Boardroom
Operational Excellence (OpEx) is no longer just about Six Sigma and manufacturing. Today, it’s a holistic management philosophy centered on creating maximum customer value while continuously improving how you deliver it.
Modern OpEx rests on four pillars:
1. Process Optimization – Using Lean, Six Sigma, and Kaizen to refine workflows and eliminate waste
2. Continuous Improvement – Fostering a culture where teams constantly seek performance gains
3. Data-Driven Decisions – Basing choices on evidence rather than gut feeling
4. Employee Empowerment – Engaging people with autonomy to drive change
Why CEOs Are Obsessed with Operational Excellence
McKinsey’s analysis of operational excellence revealed three urgent drivers making this a top C-suite priority:
- The Talent Crisis – High attrition as workers seek more purposeful, engaging work
- The Productivity Paradox – Labor productivity has stagnated despite rising costs
- The Technology ROI Gap – Two-thirds of executives are dissatisfied with technology returns
The solution? Stop automating broken processes. Process first, technology second.
Organizations that successfully implement OpEx see 33% higher revenue than competitors, significantly lower turnover, faster time-to-market, and higher customer satisfaction.
This is why process mapping isn’t optional anymore—it’s your competitive moat.
The Foundation: What Is Process Mapping?
Business Process Mapping creates visual representations of workflows, answering three questions:
- What tasks are being performed?
- Who is responsible for each task?
- When does each task occur?
The primary purpose? Making the invisible visible.
Most organizations run on “tribal knowledge”—undocumented processes existing only in key people’s heads. When that person leaves or takes vacation, chaos ensues. This is exactly why strategic process mapping drives business advancement—it externalizes critical knowledge that would otherwise be lost.
Process mapping enables teams to:
- Communicate clearly how work actually flows
- Identify hidden bottlenecks
- Uncover wasteful redundancies
- Discover optimization opportunities
The Collaborative Power
Here’s what most guides won’t tell you: The act of creating the map is often more valuable than the final diagram.
Collaborative mapping requires cross-functional input from people who actually do the work. This:
- Validates frontline staff experience
- Builds trust across silos
- Creates buy-in for future changes
- Establishes shared understanding
This makes process mapping particularly valuable when you need to bring order to organizational chaos and demonstrate concrete improvements to senior leadership.
Types of Process Maps: Choosing Your Weapon
1. Flowcharts: The Universal Starting Point
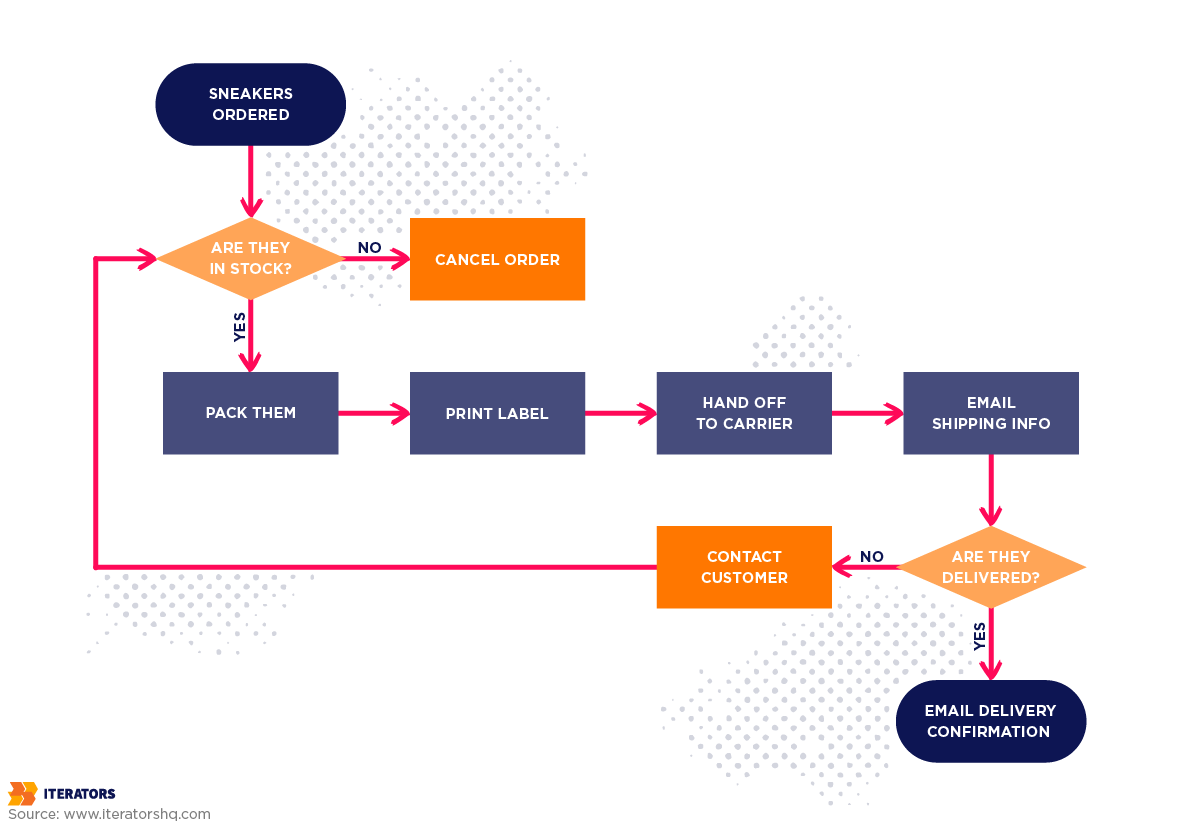
The most fundamental technique using standardized symbols (rectangles for tasks, diamonds for decisions, arrows for flow).
Best for: Documenting simple workflows, training employees, establishing baseline understanding
2. Swimlane Diagrams: Clarifying Who Does What

Enhanced flowcharts organizing steps into lanes representing specific roles, teams, or departments.
Best for: Clarifying ownership, visualizing handoffs, identifying delays at interfaces
Pro tip: Swimlane diagrams are gold for debugging cross-functional friction and presenting clear accountability structures to leadership.
3. Value Stream Mapping: The Lean Power Tool
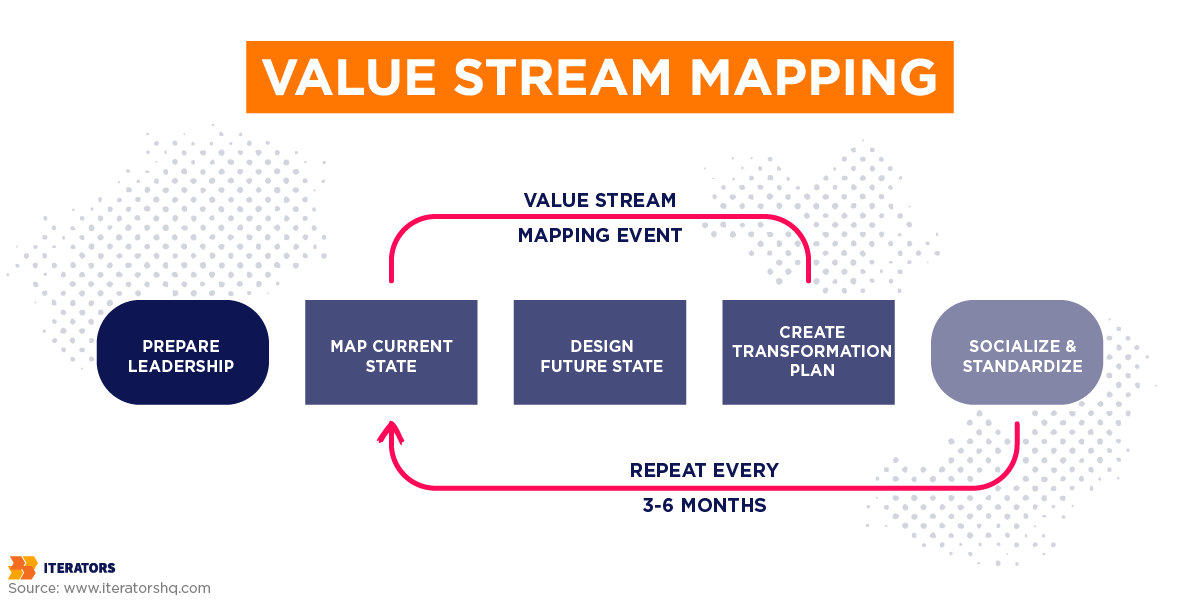
Value Stream Mapping analyzes end-to-end flow of materials and information required to deliver a product or service—a cornerstone technique of Lean methodology.
Best for: Identifying and eliminating waste, deep operational transformation, optimizing entire systems
Key metrics: Cycle Time, Lead Time, Value-Added Time, Waste
4. SIPOC Diagrams: The High-Level Overview
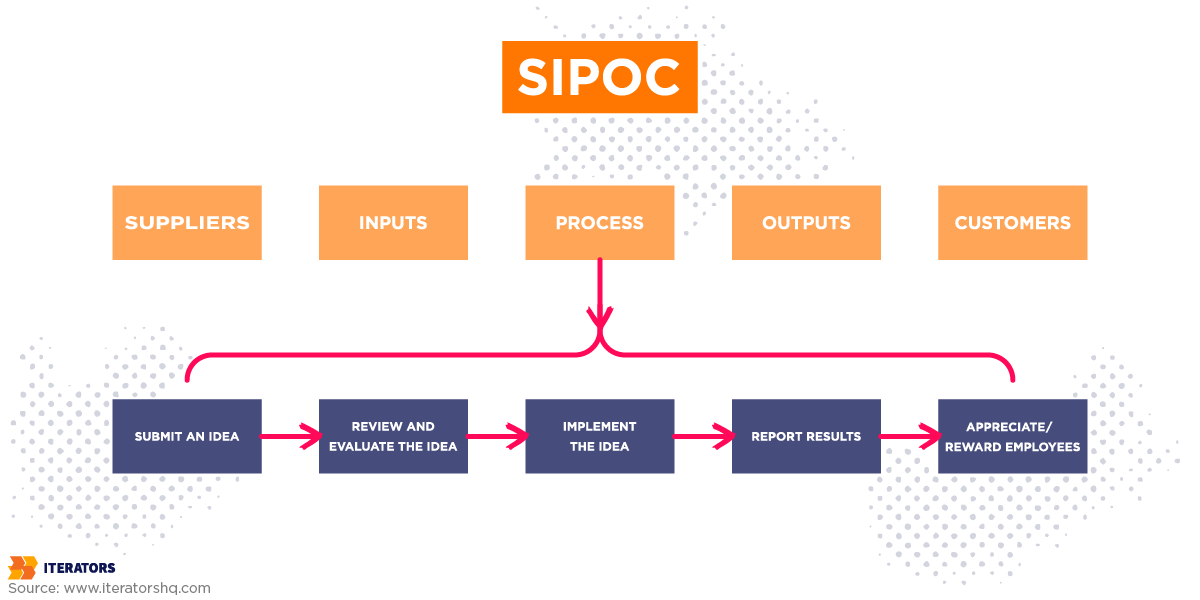
SIPOC (Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, Customers) provides a 30,000-foot view.
Best for: Defining project scope, aligning stakeholders before detailed mapping
Quick Comparison
| Map Type | Best For | Detail Level | Learning Curve |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flowchart | Simple workflows, training | Low-Medium | Very Low |
| Swimlane | Cross-functional processes | Medium | Low |
| Value Stream Map | Lean transformation | High | Medium |
| SIPOC | Project kickoff, alignment | High-Level | Very Low |
Start simple. Match the tool to the problem, not the other way around.
The Business Case: ROI of Process Mapping
The Hard Numbers
Productivity Gains: 20-50% average increase (Forrester Research)
Cost Reduction:
- 65% of organizations experience reduced costs
- 15% reduction in waste through Lean
- Up to 40% reduction in manual effort via automation
Speed and Quality:
- 50% reduction in cycle times
- 25-30% reduction in defect rates (Six Sigma)
Financial Returns:
- 20:1 typical ROI for process reengineering
- 10-15% revenue increase within first year
- 80% of BPM projects achieve >15% internal rate of return (Gartner)
Real-World Results
Healthcare: A hospital reduced psychiatric patient wait times from 3.8 hours to 1.6 hours (58% reduction) in three weeks by mapping and redesigning information flow.
Manufacturing: 40% reduction in lead times, 25% reduction in inventory costs, 98% on-time delivery after supply chain process mapping.
FinTech: A UK bank discovered through journey mapping that their system rejected forms with special characters in names (O’Brien, María). Fixing this single issue significantly improved conversion rates.
How to Implement Process Mapping: A Step-by-Step Framework
Now for the practical part. Following proven process improvement methodologies, successful process mapping initiatives follow a structured, collaborative framework.
Step 1: Define Scope and Purpose
Set a specific goal (e.g., “Reduce onboarding time by 30%”), establish clear boundaries, and document what’s in/out of scope.
If you can’t articulate a clear business outcome, don’t start yet.
Step 2: Assemble a Cross-Functional Team
Include frontline employees who execute the process daily, process owners, and a facilitator. Don’t map in isolation from the people doing the actual work—management often has idealized views that don’t match operational reality.
Step 3: Document the Current (“As-Is”) Process
Run collaborative workshops, observe work directly, and document every step including workarounds. Map reality, not the idealized handbook version.
Step 4: Analyze for Improvement Opportunities
Look for:
- Bottlenecks where work piles up
- Redundant tasks
- Unnecessary steps adding no customer value
- Excessive handoffs
- Unclear decision criteria
Step 5: Design the Future (“To-Be”) Process
Eliminate unnecessary steps, combine or reorder remaining steps, introduce smart automation, and clarify roles.
Perfect is the enemy of good. Design for significant improvement, not perfection.
Step 6: Implement and Monitor
Pilot with a small team first, track key metrics (cycle time, error rate, satisfaction), and create feedback mechanisms for quick adjustments.
Step 7: Review and Refine Continuously
Schedule regular reviews (quarterly for critical processes), update maps when changes occur, and treat maps as living documents.
Best Tools for Process Mapping in 2024
Quick Decision Framework
Small Organizations (<50 people): Start with Diagrams.net (free) or Miro (collaborative, $8/user/month)
Mid-size (50-500): Use Miro or Lucidchart ($7.95/user/month) for mapping; add Process Street for operational playbooks
Enterprise (500+): Consider Signavio or Celonis for process mining; Lucidchart or Visio for formal documentation
Technical Teams: Use Miro or FigJam integrated with Jira/Confluence
The Iterators take: We use Miro for workshops—the template library is excellent and real-time collaboration actually works.
Process Mapping for Technology Operations
The Agile Paradox
Many teams resist process mapping, fearing bureaucracy. But Agile is not anti-process—it’s anti-waste.
Process mapping makes bottlenecks visible, enables rapid experimentation, facilitates transparent retrospectives, and helps eliminate non-value-adding activities.
Kanban Boards: Living Process Maps
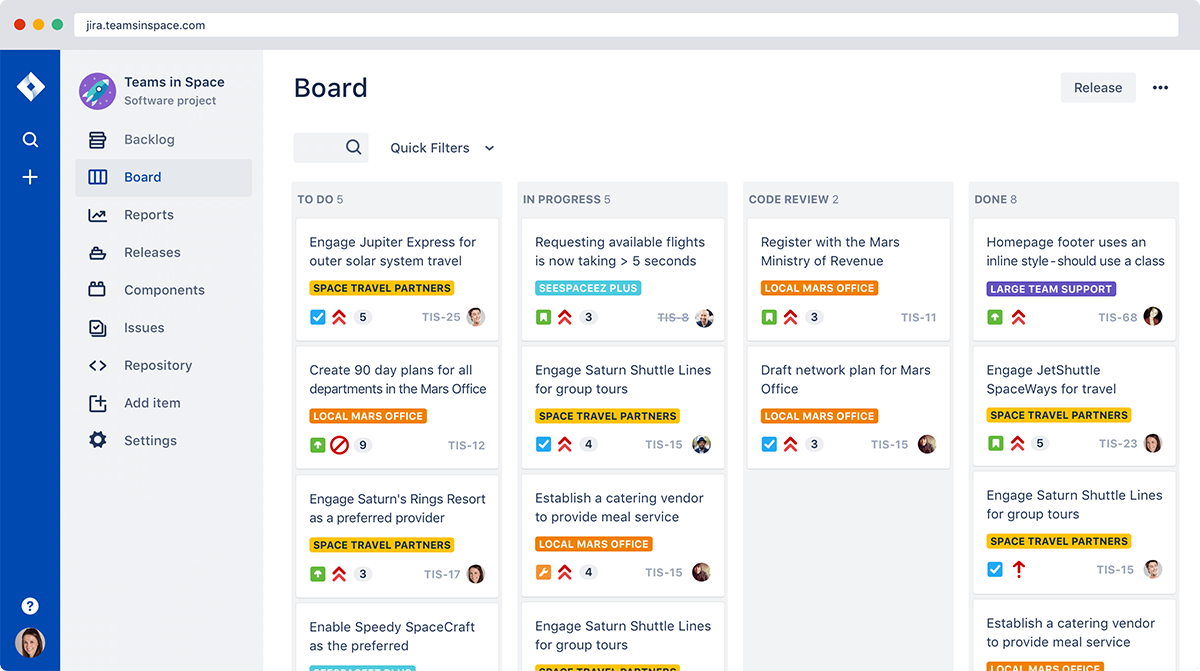
A Kanban board is fundamentally a real-time process map. Visualizing workflow stages makes bottlenecks immediately apparent, WIP limits force focus, and flow metrics emerge naturally.
Value Stream Mapping for DevOps
For organizations implementing DevOps consulting practices, value stream mapping is exceptionally powerful for optimizing Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipelines.
Map your CI/CD pipeline from developer commit to production deployment. Track processing time, wait time, and % complete & accurate for each step.
Real example: An Iterators client had:
- Lead Time: 14 days
- Cycle Time: 4 hours
- Process Efficiency: 1.2%
That means 98.8% was spent waiting. After addressing bottlenecks: Lead Time dropped to 2 days (85% reduction), efficiency improved 7x.
Mapping Sprint Workflows
Within the Scrum framework, a process flow diagram can visualize the entire sprint cycle from Product Backlog through Sprint Planning, development work with Daily Stand-ups, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective.
Common discoveries when mapping sprints:
- Sprint Planning takes 4 hours because requirements aren’t refined beforehand
- Daily Stand-ups turn into status reports instead of coordination sessions
- Retrospectives don’t lead to action items
- Sprint Reviews happen without stakeholder participation
The fix: Map the flow, identify the breakdowns, design improvements.
Key Metrics for Technology Process Mapping

When mapping technology operations, track these metrics:
Flow Metrics:
- Flow Time: How long work takes from start to finish
- Flow Velocity: How many items are completed per time period
- Flow Efficiency: Percentage of time spent on value-adding work vs. waiting
DORA Metrics (for DevOps):
- Deployment Frequency: How often you deploy to production
- Lead Time for Changes: Time from commit to production
- Change Failure Rate: Percentage of deployments that cause incidents
- Time to Restore Service: How quickly you recover from failures
Kanban Metrics:
- Cycle Time: Time from “In Progress” to “Done”
- Throughput: Number of items completed per sprint
- WIP (Work in Progress): Number of items actively being worked on
The Iterators principle: Don’t track metrics for the sake of tracking. Track metrics that help you make decisions. If a metric doesn’t lead to action, stop measuring it.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them

Process mapping initiatives often fail not because of flawed techniques, but because of fundamental errors in approach and execution. These pitfalls are primarily rooted in failures of change management, communication, and strategic alignment.
Let’s talk about the mistakes we see over and over—and how to avoid them.
Pitfall 1: Mapping Without Clear Purpose
Fix: Define a SMART goal before starting. No mapping without measurable objectives.
Pitfall 2: Excluding Frontline Employees
Fix: Involve the “doers” from day one. Create psychological safety to share reality including workarounds.
Pitfall 3: Mapping the Ideal vs. Real
Fix: Ask “Tell me about the last time you did this. Walk me through exactly what happened.”
Pitfall 4: Over-Complicating the Map
Fix: Start simple. If your map doesn’t fit on one screen, it’s too detailed.
Pitfall 5: Treating Maps as Static
Fix: Assign ownership, schedule regular reviews, integrate into onboarding, update when processes change.
From Process Mapping to Continuous Improvement Culture
Process mapping is the catalyst, not the conclusion. The ultimate goal? Evolve into a self-sustaining culture where every employee enhances how work gets done.
The Four Pillars
1. Leadership Commitment: Leaders model the behaviors, not just delegate initiatives
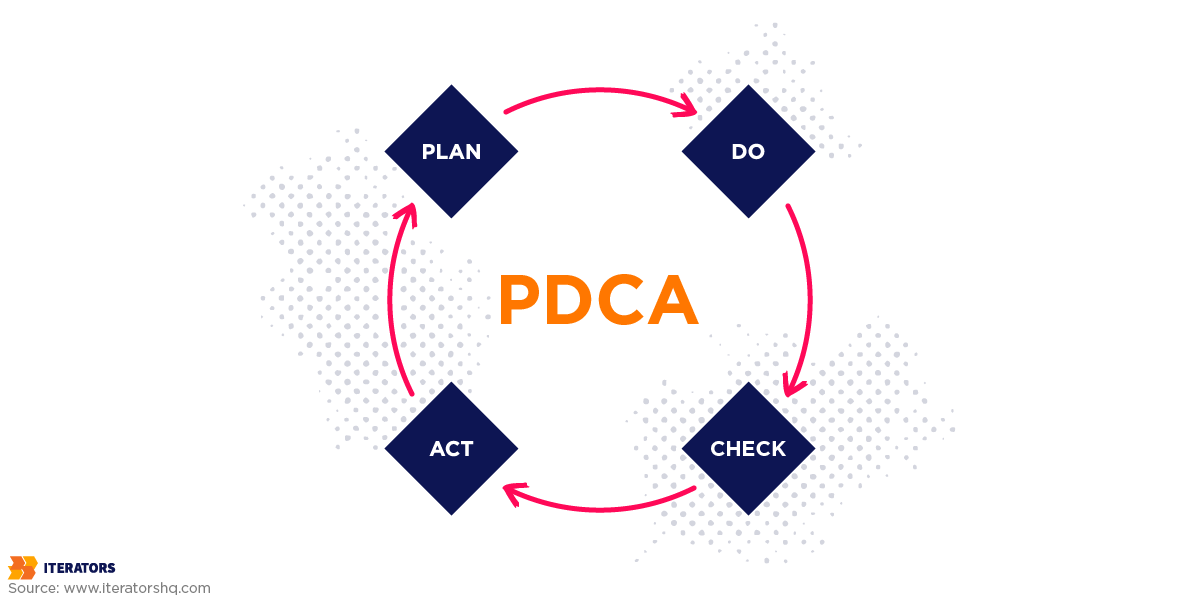
2. Building Feedback Loops: Use PDCA cycles, sprint retrospectives, and metrics dashboards that lead to action
3. Training Teams: Equip employees with process thinking, mapping techniques, and root cause analysis
4. Integrating Reviews: Make process improvement a routine part of operations, not an extra
The transformation timeline: Expect 12-24 months to move from discrete projects to continuous improvement culture.
The Future: AI and Intelligent Process Mapping
AI-Driven Automation
AI tools using NLP can analyze meeting transcripts and documents to automatically generate process maps in hours instead of weeks. Example tools: Skan.ai, Celonis, IBM Process Mining.
Process Mining: Discovering Reality
Process mining algorithms analyze event logs from enterprise systems to construct detailed maps of how processes actually execute—including variations, deviations, and bottlenecks.
When combined with AI:
- Automated root-cause analysis
- Predictive analytics
- Generative AI copilots for plain-language queries
The New Operating Model
Traditional: Manual mapping → Design → Implement → Monitor → Repeat in 1-2 years
Intelligent: AI continuously monitors → Detects deviations → Recommends improvements → Teams validate → Measure impact → Repeat continuously
The “To-Be” process becomes a dynamic state that evolves continuously.
Industry-Specific Applications
FinTech: Compliance and Customer Experience
Key applications: KYC/AML compliance documentation, customer journey optimization, fraud detection workflows, payment processing optimization
Case study: UK bank used journey mapping to discover backend errors rejecting special characters in customer names, significantly improving conversion after fixing.
HealthTech: Patient Outcomes and Safety

Key applications: Patient journey mapping, HIPAA compliance workflows, clinical quality measures, supply chain optimization
Case study: Hospital reduced psychiatric patient wait times 58% (3.8 to 1.6 hours) by redesigning information flow—zero additional staff.
Growing Companies: Scaling Without Chaos
Key applications: Creating scalable playbooks, optimizing customer onboarding, building structure that enables speed not bureaucracy
The approach: Map 3-5 high-impact processes, keep simple and visual, iterate quickly, empower teams.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between process mapping and workflow automation?
Process mapping visualizes workflows (the blueprint). Workflow automation implements technology to execute them (the construction). Always map and optimize before automating.
How long to see results?
Days: Team alignment, obvious bottlenecks identified
Weeks: Simple improvements implemented, measurable gains
Months: Cultural shift, sustained productivity gains
Most clients see results within 30-60 days.
Do small organizations need this?
Yes, but keep it simple. Map your 3-5 critical processes. Use them for onboarding and training. Update as you grow.
How to get team buy-in?
Start with their pain points, involve people from the beginning, show quick wins, frame as “make your job easier,” and celebrate contributors.
What about creative/non-linear workflows?
Even creative work has processes. Map decision points, feedback loops, collaboration patterns, and quality gates. The goal is eliminating friction around creativity, not eliminating creativity.
How often to update maps?
High-change processes (technology, customer-facing): Quarterly
Moderate-change (HR, finance): Annually
Stable processes: As needed
Update whenever the map no longer reflects reality.
Conclusion: From Invisible Chaos to Visible Excellence
You can’t optimize what you can’t see.
Process mapping transforms invisible workflows into visible opportunities, aligns teams, identifies waste, builds continuous improvement culture, and achieves measurable results like 20:1 ROI and 50% cycle time reductions.
Your Next Steps
Getting started: Pick one painful process, gather the people who execute it, map it on a whiteboard, identify top 3 bottlenecks, fix one this week.
Scaling up: Establish review cadences, train teams, integrate into OKRs, invest in collaborative tools, track key metrics.
Enterprise: Conduct maturity assessment, identify critical value streams, implement process mining, build a center of excellence.
The Iterators Commitment
We don’t just consult—we build. Through our custom software development services, we design and develop solutions that embed operational excellence into your workflows, optimize DevOps pipelines to eliminate waste, build data infrastructure for AI-powered optimization, and implement systems that make continuous improvement sustainable.
Because here’s the truth: Process mapping reveals opportunities. But you need the right technology infrastructure to capitalize on them.
Ready to Transform Your Operations?
We’ll help you identify high-impact opportunities, design a roadmap for operational excellence, and build the custom software and DevOps infrastructure to make it real.
No fluff. No shelf-ware. Just measurable results.
Schedule a free consultation with Iterators →

Operational excellence isn’t about working harder—it’s about building smarter systems. And that’s exactly what we do.
