The 2021 Suez Canal blockage didn’t just strand a ship—it exposed the fragility of global commerce. For six days, the Ever Given held $400 million per hour hostage while supply chain managers worldwide scrambled with outdated tracking systems and fragmented data. AI blockchain integration for supply chain operations could have prevented this chaos by providing real-time visibility and autonomous rerouting capabilities. The answer reveals why this technological convergence isn’t just innovation—it’s survival.
Modern supply chains are drowning in what experts call a “permacrisis.” Geopolitical shocks, climate disruptions, and post-pandemic volatility have made traditional logistics models obsolete. Companies now lose an average of $184 million annually to supply chain disruptions, with U.S. organizations shouldering approximately $228 million per year. These aren’t just numbers—they’re the cost of operating blind in an interconnected world that demands real-time visibility.
AI blockchain integration for supply chain management addresses what industry leaders call the “Trilemma of Supply Chain Modernization”: Speed, Cost, and Trust. While blockchain provides the immutable “Truth”—a decentralized, tamper-proof ledger—AI provides the “Intelligence”—predictive analytics and autonomous agents. Together, they enable the shift from reactive supply chains that scramble after disruptions to cognitive supply chains that predict problems and execute solutions automatically.
Ready to explore AI blockchain integration for supply chain solutions? Schedule a consultation with Iterators to discuss how we can build custom integration solutions tailored to your business needs.
The Financial Reality of Supply Chain Fragility
Let’s talk money. The financial impact of supply chain vulnerability is severe and measurable. In 2024, nearly 80% of organizations experienced major supply chain disruptions, with most facing between one and ten critical incidents within twelve months. These aren’t isolated problems—they’re systemic failures caused by lack of visibility.
Here’s how the damage breaks down:
- Revenue Loss: 36% of companies report direct revenue loss from stockouts and inability to fulfill orders during disruptions
- Reputational Damage: 41% received customer complaints, signaling long-term brand erosion that often exceeds immediate financial losses
- Administrative Costs: Tens of billions globally consumed by manual reconciliation, disputed invoices, and paper-based compliance checks
The Suez Canal incident perfectly demonstrates this failure. While the blockage was physical, the cascading economic damage was an information failure. Machine learning systems in place at the time couldn’t prevent the incident or effectively reroute traffic in real-time because they lacked a unified, trusted view of the network.
According to McKinsey’s research on Supply Chain 4.0, AI systems were operating on siloed data, unable to “see” the compounding variables that led to the grounding. An AI blockchain integration for supply chain monitoring providing real-time, immutable state of the entire maritime network could have enabled AI models to predict congestion risks and autonomously reroute vessels days in advance.
This underscores a central truth: AI is only as intelligent as the data it consumes, and current supply chain data is fragmented and unreliable.
Building Resilience Without Breaking Your Budget
Chief Supply Chain Officers face a new mandate. Companies no longer prioritize the lowest cost per unit if it sacrifices robustness. But building resilience typically costs more—higher inventory carrying costs and redundant supplier contracts.
The promise of AI blockchain integration for supply chain operations? Lowering the “resilience premium.”
Instead of physical redundancy (warehouses stuffed with safety stock), you get information superiority (knowing exactly where every unit is and when it will arrive). This approach, similar to digital transformation strategies, lets you achieve resilience without exploding your balance sheet.
Blockchain technology alone can reduce administrative costs by up to 30%. When you add AI-driven demand forecasting fed with accurate blockchain data, you reduce warehousing costs by 5-10% and inventory holding costs by up to 25% through automated restocking smart contracts.
How AI Blockchain Integration for Supply Chain Actually Works
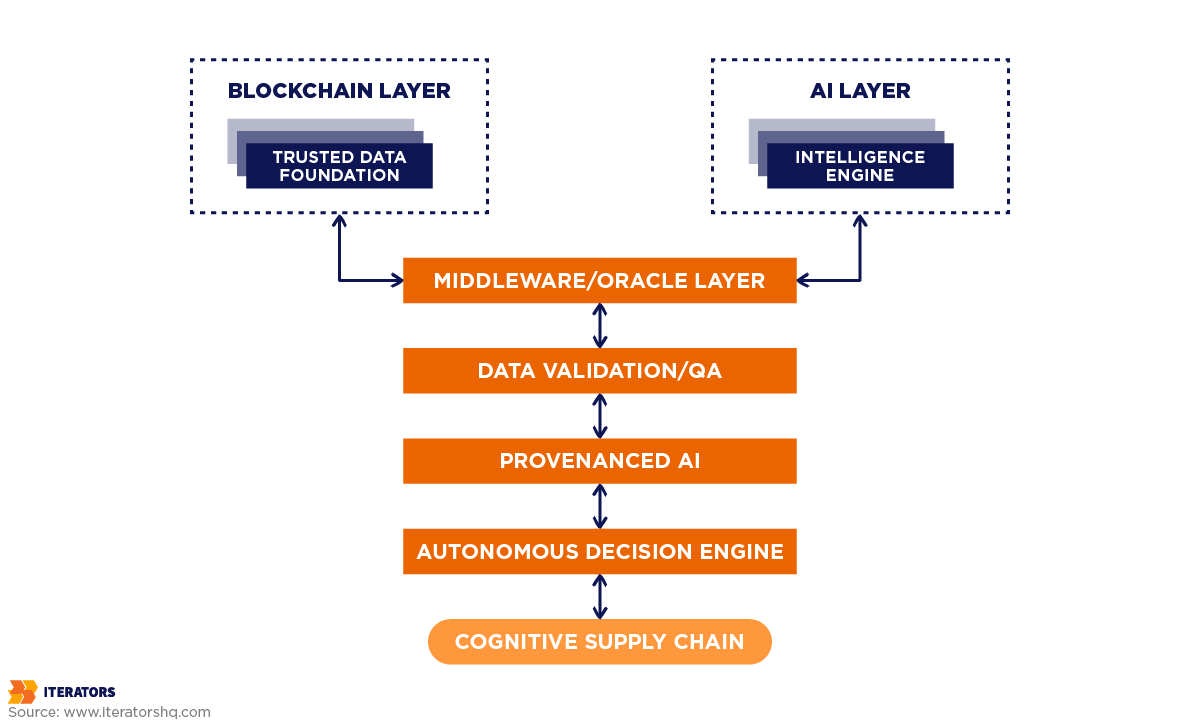
Let’s cut through the hype. AI blockchain integration for supply chain isn’t magic—it’s smart architecture. These technologies work on different layers of your software system:
- Blockchain: The Data and Settlement Layer
- AI: The Compute and Analysis Layer
Blockchain: Your Immutable Foundation
In supply chain contexts, blockchain isn’t about cryptocurrency. It’s about Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)—a shared, append-only database that no single participant controls, yet all can verify. Similar to how blockchain disrupts traditional supply chains, this creates unprecedented transparency.
Key Technical Features:
Decentralization: Unlike a centralized ERP system managed by one company (creating a single point of failure), blockchain distributes the ledger across a network of nodes—suppliers, logistics providers, and banks.
Immutability: Once a transaction (e.g., “Container #102 loaded on Ship A”) is recorded and validated by consensus, it cannot be altered. This eliminates the “he said, she said” disputes that plague logistics.
Smart Contracts: Automated scripts stored on the blockchain that execute actions when conditions are met. A smart contract can release payment to a supplier the exact second a goods receipt is verified, removing net-30 or net-60 payment delays.
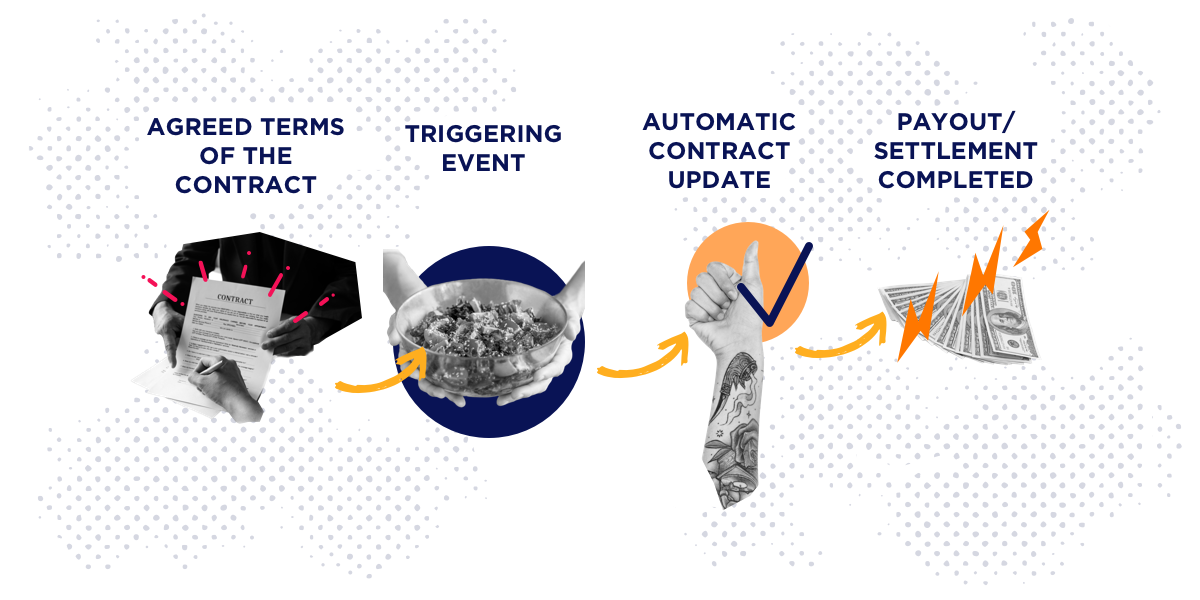
Platform Choice: Hyperledger Fabric vs. Ethereum
Research on AI and blockchain convergence reveals a split in platform preferences:
Hyperledger Fabric dominates enterprise supply chains (Walmart, Maersk). It’s a permissioned blockchain where participants must be known and authenticated. Its standout feature? “Channels”—allowing subgroups of participants (like a buyer and specific supplier) to share private data invisible to the rest of the network. This privacy is critical for protecting pricing strategies.
Ethereum/Polygon: Public blockchains or Layer-2 scaling solutions work well for “track and trace” scenarios where public transparency is valuable (proving coffee is fair trade). However, transaction fees and data privacy issues often relegate public chains to the settlement layer rather than the data layer for high-volume logistics.
Artificial Intelligence: Your Predictive Engine
If blockchain provides the “trusted memory,” AI provides the “brain.” Supply chain data is noisy, high-volume, and complex. AI makes sense of it.
Core AI Functions in AI Blockchain Integration for Supply Chain:
Predictive Analytics: Neural networks forecast demand, weather disruptions, and maintenance needs. Research shows AI can reduce forecasting errors by 20-50%, leading to a potential 65% reduction in lost sales from out-of-stock scenarios.
Computer Vision: Analyzing video feeds from warehouses or imaging of products (diamonds, fruit) to verify quality and authenticity without human intervention.
Agentic AI: The next frontier. By 2030, Gartner predicts 50% of supply chain solutions will employ intelligent agents capable of autonomous negotiation and execution. These agents don’t just predict delays—they re-book freight and update the blockchain ledger automatically.
Connecting the Systems: The Oracle Solution
Here’s the fundamental challenge: blockchains are isolated—they cannot access data outside their network. AI models typically run off-chain due to high computational requirements. Bridging this gap requires Middleware—specifically, Oracles.
Chainlink has emerged as the industry-standard infrastructure for AI blockchain integration for supply chain systems. Chainlink nodes act as secure bridges fetching data from the real world (IoT sensors, weather APIs, AI results) and delivering it to blockchain smart contracts.
| Feature | Blockchain Contribution | AI Contribution | Integrated Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Integrity | Immutable record, single source of truth | Detects dirty data entry | Trusted Data Foundation |
| Traceability | End-to-end audit trail | Pattern recognition to identify fraud | Proactive Fraud Prevention |
| Automation | Smart contracts for execution | Predictive triggers | Autonomous Supply Chain |
| Privacy | Zero-knowledge proofs | Federated learning on private data | Collaborative Intelligence |
Solving AI’s Data Quality Problem
One of the most important insights about AI blockchain integration for supply chain is how blockchain solves AI’s fundamental weakness: Data Quality.
AI models make poor predictions if fed inaccurate or manipulated data. In fragmented supply chains, bad data is everywhere—suppliers may falsify inventory reports, or temperature sensors may be tampered with.
Blockchain acts as a cryptographic anchor for data. By securing data at the source (signing a temperature reading when the IoT device captures it) and storing that signature on the ledger, the system ensures data integrity. When the AI model uses this data for training or predictions, it can verify mathematically that the data hasn’t been altered since creation.
This leads to “Provenanced AI”—every insight generated by the model can be traced back to verified, immutable data.
Furthermore, AI blockchain integration for supply chain enables Federated Learning. In this approach, AI models are trained across multiple locations (different warehouses) without exchanging raw data. Only model updates are shared and recorded on the blockchain.
This allows competing companies to collaborate on training a global supply chain optimization model without ever revealing specific shipment volumes or supplier lists to each other. According to Forbes research on AI and blockchain transformation, it’s collaborative intelligence without corporate espionage.
Real-World Success Stories
Walmart and IBM Food Trust: Speed That Saves Lives
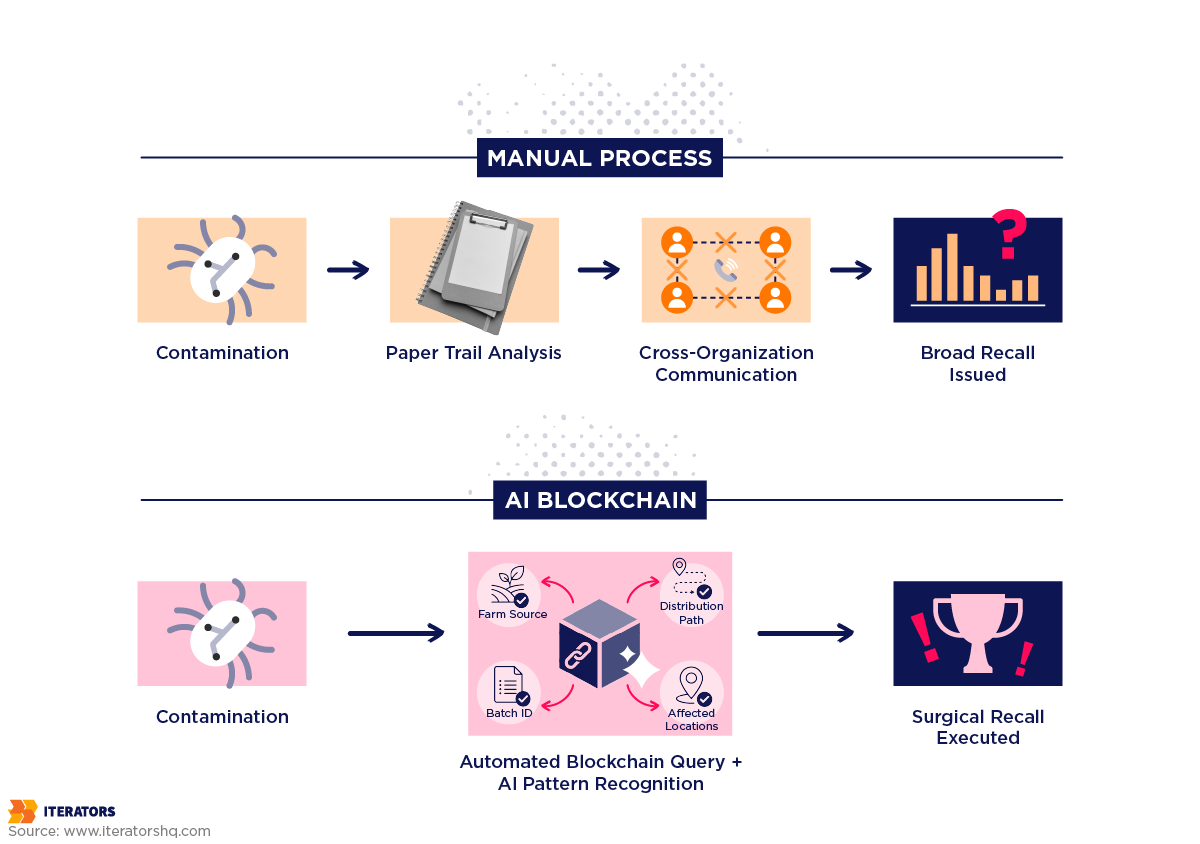
The Problem: After several E. coli outbreaks, Walmart struggled to trace contaminated leafy greens back to their source. The paper-based method took nearly a week—requiring broad, panic-induced recalls of safe products, costing millions and destroying consumer trust.
The AI Blockchain Integration for Supply Chain Solution: Walmart partnered with IBM to build the Food Trust platform using Hyperledger Fabric. This permissioned blockchain requires suppliers to upload data at every harvest and processing event.
The Results:
- Traceability Speed: Time required to trace the source of a specific package of mangoes or spinach reduced from 7 days to 2.2 seconds
- Precision: Walmart can now issue “surgical recalls,” removing only specific batches from specific farms rather than clearing entire shelves nationwide
- Adoption: The system scaled to include major suppliers like Dole and Driscoll’s
AI Integration: AI analyzes shelf-life data of fresh produce entered into the system, optimizing inventory rotation to reduce spoilage waste.
De Beers Tracr: Digital Twins Meet Physical Products
The Problem: The diamond industry has long been plagued by “conflict diamonds” and difficulty distinguishing natural stones from high-quality synthetics.
The Solution: De Beers launched the Tracr platform—a sophisticated synthesis of AI, IoT, and Blockchain demonstrating effective AI in blockchain applications.
The Mechanism:
- AI Scanning: At the mine, rough diamonds are scanned. AI algorithms analyze the stone’s physical characteristics to create a unique “Digital Twin” or ID.
- Blockchain Tracking: This ID is recorded on the blockchain. As the stone is cut and polished, the digital twin is updated.
- Verification: Even if the stone is cut into smaller pieces, AI algorithms can link the polished output back to the original rough stone’s blockchain record.
The Results:
- Scale: The platform registers over 1 million diamonds per week
- Market Impact: As of 2025, De Beers provides country-of-origin data for all registered diamonds over one carat—a level of transparency that’s become a premium market differentiator
Maersk and TradeLens: The Cautionary Tale
Not every AI blockchain integration for supply chain succeeds, and understanding why is valuable.
The Context: Maersk and IBM launched TradeLens to digitize the global Bill of Lading process, aiming to replace paper with a blockchain ledger.
The Outcome: Despite processing millions of events, TradeLens was discontinued in early 2023.
Root Cause Analysis:
Governance Failure: The platform was perceived as a “Maersk product.” Competitor shipping lines were reluctant to join a platform where their data might be visible to their biggest rival.
Misaligned Incentives: While ocean carriers benefitted from efficiency, freight forwarders and shippers saw increased costs without sufficient immediate return on investment.
Strategic Lesson: For AI blockchain integration for supply chain to succeed, platforms must be network-neutral. Future solutions will likely rely on independent consortia where governance is shared rather than owned by one company.
This is the “TradeLens Trap”—brilliant technology undermined by poor governance. Don’t let it happen to you.
The Business Case: ROI That Matters

For CTOs and VPs, technology must show balance sheet impact. Research supports a strong ROI case based on cost reduction, risk mitigation, and revenue protection—similar to the business metrics that drive growth.
Cost Reduction Metrics
Administrative Efficiency: Implementing blockchain documentation flows can reduce supply chain administrative costs by 30%. This comes from eliminating manual data entry, reconciliation of conflicting ledgers, and physical document handling.
Inventory Optimization: AI-driven demand forecasting, when fed with accurate blockchain data, reduces warehousing costs by 5-10% and inventory holding costs by up to 25% through automated restocking smart contracts.
Risk Mitigation and Insurance
Fraud Reduction: With supply chain fraud (including cargo theft and invoice fraud) costing the industry approximately $400 billion annually, the immutability of blockchain acts as digital insurance. Smart contracts prevent invoice fraud by requiring cryptographic proof of delivery before payment release.
Disruption Avoidance: Disruptions cost $184 million annually. If AI blockchain integration for supply chain prevents just one major disruption (by predicting supplier insolvency weeks in advance), the system pays for itself immediately.
ROI Timeline
Based on industry implementations, the ROI timeline typically follows a three-stage curve:
| Phase | Duration | Investment Focus | ROI / Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pilot | 1-3 Months | MVP Development, Cloud Setup | Proof of concept, Stakeholder buy-in |
| Deployment | 4-9 Months | Integration with ERP, IoT | Admin savings (30%), Visibility |
| Optimization | 10-18 Months | AI Model Training, Automation | Inventory reduction (10%), Lower risk |
| Maturity | 18+ Months | Network Expansion, Ecosystem | Market differentiation, Brand Trust |
Building Your Technology Stack
Implementing AI blockchain integration for supply chain requires navigating a “build vs. buy” decision and orchestrating multiple technologies. Here’s what works in production:
The Core Components
Blockchain Layer:
- Hyperledger Fabric recommended for enterprise consortiums due to privacy channels and high speed
- Ethereum (via Layer 2s like Polygon or Arbitrum) works for public-facing transparency
Smart Contract Language:
- Chaincode (Go/Node.js) for Fabric
- Solidity for Ethereum-compatible chains
AI Frameworks:
- TensorFlow or PyTorch for model development
- These models run off-chain on cloud infrastructure (AWS SageMaker, Azure ML)
Middleware:
- Chainlink essential for managing connections between off-chain AI models and on-chain smart contracts
- Without this, the blockchain can’t access the AI’s insights
Cloud Infrastructure
Your AI blockchain integration for supply chain needs robust cloud infrastructure, similar to managing technical infrastructure handovers:
- AWS: Managed Blockchain service, SageMaker for ML, IoT Core for sensor data
- Azure: Blockchain Workbench, Machine Learning Studio, IoT Hub
- Google Cloud: Cloud Spanner for distributed databases, Vertex AI for ML
The choice often depends on existing enterprise agreements and where your current data lives.
Your Implementation Roadmap
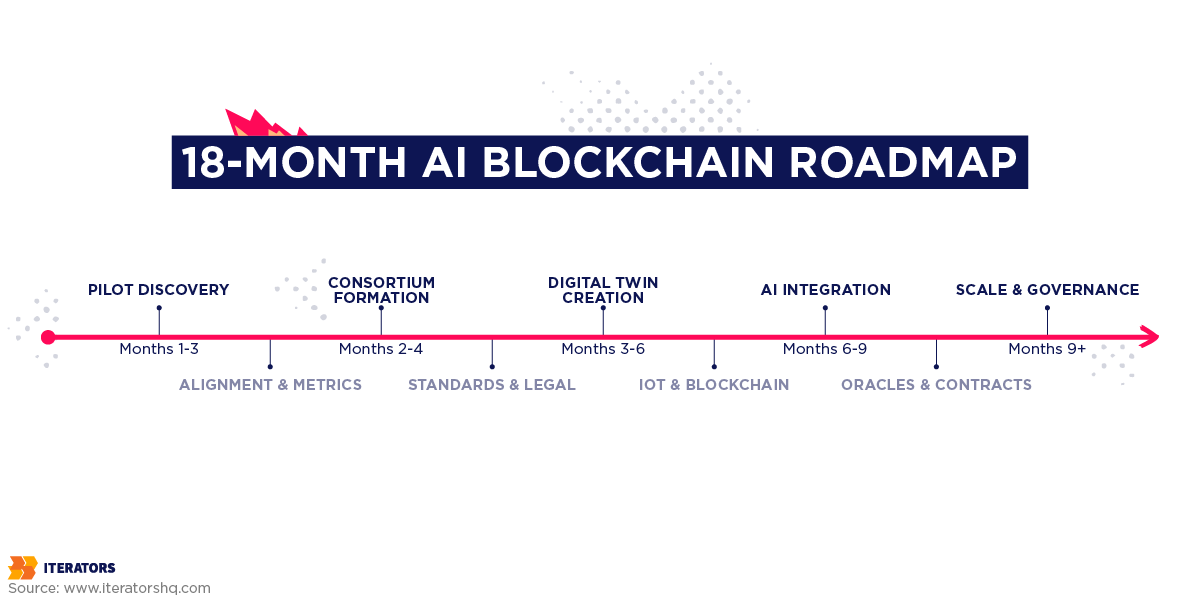
Implementing AI blockchain integration for supply chain is complex but manageable. Here’s the battle-tested roadmap we use at Iterators:
Step 1: Pilot Discovery (Month 1-3)
Identify a single, high-friction pain point. Don’t try to do everything at once.
Example: “Invoice reconciliation with Supplier X takes 3 weeks and requires 5 people manually matching documents.”
Deliverables:
- Pain point documentation
- Current vs. desired state mapping
- Success metrics definition
- Stakeholder alignment
| ESSENTIAL FOR MVP Launch in 3-6 Months | PHASE 2 ENHANCEMENTS Scale After Proof of Value |
|---|---|
| Single Supplier Blockchain Integration Connect one key supplier to permissioned Hyperledger Fabric network for proof of concept | Multi-Tier Supplier Network Expand to 10+ suppliers across multiple geographic regions and product categories |
| IoT Temperature/GPS Sensors Deploy sensors for one high-value product category (pharmaceuticals or perishables) | Computer Vision Quality Verification AI-powered image analysis for automated product authentication and defect detection |
| Basic Smart Contract for Payment Automate payment release upon verified delivery confirmation | Autonomous Routing AI Agents Deploy agentic AI for automatic rerouting decisions without human approval |
| Simple AI Demand Forecasting Train ML model on 12-24 months historical data for one product line | Full ERP Bidirectional Integration Write data back to ERP, enabling closed-loop automation across systems |
| Chainlink Oracle Integration Connect off-chain AI predictions to on-chain smart contracts | Zero-Knowledge Proof Privacy Implement ZKP protocols for sensitive data verification without exposure |
| ERP Integration (Read-Only) Pull data from existing SAP/Oracle system without modifying core infrastructure | Public Blockchain Transparency Layer Add Ethereum/Polygon integration for customer-facing product provenance |
| 3-Party Consortium Governance Establish framework with your company, one supplier, one logistics provider | DAO Governance Structure Transition to decentralized autonomous organization with token-based voting |
| Pilot Metrics Dashboard Track traceability speed, cost savings, and disruption prevention in real-time | Quantum-Resistant Cryptography Future-proof blockchain security with post-quantum encryption algorithms |
| 💡 Start Here: Focus on these 8 capabilities to prove ROI within 6-12 months. Average pilot investment: $50K-$150K | 🚀 Scale Later: Add these features after demonstrating 30% admin cost reduction and 2.2-second traceability |
Step 2: Consortium Formation (Month 2-4)
Form a “Minimum Viable Ecosystem” (MVE) consisting of:
- Your company
- One key supplier
- One logistics provider
Agree on data standards (GS1 is industry standard for product identification).
Critical Success Factor: Get legal and procurement teams involved early. They’ll need to draft data-sharing agreements and establish governance frameworks.
Step 3: Digital Twin Creation (Month 3-6)
Deploy IoT sensors to capture the physical state of goods and anchor this data to the blockchain, similar to implementing AI personal assistants.
Example Implementation:
- Temperature sensors on refrigerated containers
- GPS trackers on shipments
- RFID tags on individual products
Each sensor reading is secured and recorded on the blockchain with a timestamp and location.
Step 4: AI Integration (Month 6-9)
Once reliable data is flowing, train ML models to detect problems in the data stream.
Example Models:
- Predictive maintenance for fleet vehicles
- Demand forecasting based on historical patterns
- Route optimization considering weather and traffic
Connect the ML output to a smart contract via Chainlink. When the AI detects a problem (predicted delay), the smart contract automatically notifies affected parties and potentially triggers alternative routing.
Step 5: Scale and Governance (Month 9+)
Expand the network. Move from centralized governance (for the pilot) to decentralized governance (for the ecosystem) to avoid the “TradeLens Trap.”
Governance Considerations:
- Who validates new participants?
- How are disputes resolved?
- What happens when participants want to leave?
- How are upgrades decided and implemented?
Overcoming Technical Challenges

Let’s be honest about the obstacles. Every AI blockchain integration for supply chain faces these challenges:
Blockchain Speed Limitations
The Problem: Public blockchains like Ethereum can process 15-30 transactions per second. Your supply chain might need thousands.
The Solution:
- Use Layer 2 solutions (Polygon, Arbitrum)
- Implement Hyperledger Fabric with optimized channel architecture
- Consider hybrid approaches where only critical events hit the blockchain
Data Privacy and Compliance
The Problem: GDPR, HIPAA, and other regulations create complex requirements for data handling, similar to SOC 2 compliance challenges.
The Solution:
- Use Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) to verify data without revealing it
- Implement Hyperledger Fabric’s private data collections
- Store sensitive data off-chain with only hashes on-chain
- Work with legal teams to ensure “right to be forgotten” compliance
Integration with Legacy Systems
The Problem: Your ERP system from 2005 doesn’t speak blockchain.
The Solution:
- Build middleware layers (APIs, message queues)
- Use enterprise service buses (ESBs) as translation layers
- Implement gradual migration strategies
- Consider the “Strangler Fig” pattern—slowly replacing legacy functionality
Cost and Resource Requirements
The Problem: Blockchain and AI development isn’t cheap.
The Solution:
- Start with pilot projects to prove ROI
- Use managed services to reduce infrastructure overhead
- Partner with experienced development teams (like Iterators) rather than building expertise from scratch
- Calculate total cost of ownership vs. cost of disruptions
At Iterators, we’ve built AI blockchain integration for supply chain solutions for enterprise clients across fintech, logistics, and e-commerce. Our team combines deep expertise in distributed systems, machine learning, and enterprise integration. Contact us to discuss how we can accelerate your implementation.
Industry-Specific Applications
Different industries face unique challenges that AI blockchain integration for supply chain solves in specific ways:
Food and Beverage
Challenge: Contamination traceability, cold chain monitoring, compliance documentation
Solution:
- Blockchain tracks every touchpoint from farm to table
- AI predicts spoilage based on temperature and time data
- Smart contracts automatically trigger recalls for specific batches
Example: Walmart’s 2.2-second trace time vs. 7-day manual process
Pharmaceuticals
Challenge: Counterfeit drugs, temperature-sensitive shipments, regulatory compliance
Solution:
- Blockchain creates immutable chain of custody
- AI detects anomalies in packaging or routing
- Smart contracts enforce compliance checkpoints
Market Impact: Counterfeit drugs represent 10% of global pharmaceutical market—blockchain can eliminate this entirely
Automotive
Challenge: Complex multi-tier supplier networks, just-in-time delivery, quality control
Solution:
- Blockchain tracks parts from raw materials to assembly
- AI predicts supplier delays based on historical patterns
- Smart contracts manage payment releases based on quality verification
Luxury Goods
Challenge: Authentication, provenance verification, gray market prevention
Solution:
- Blockchain creates “digital passports” for products
- AI analyzes physical characteristics for verification
- Smart contracts manage ownership transfers
Example: De Beers Tracr platform processing 1 million diamonds weekly
The Future of AI Blockchain Integration for Supply Chain

The convergence of AI and blockchain in supply chains is accelerating. Here’s what the next 3-5 years will bring:
Autonomous Supply Chain Agents
By 2030, Gartner predicts 50% of supply chain solutions will include agentic AI capabilities. These aren’t just prediction engines—they’re autonomous agents that:
- Negotiate with suppliers based on predefined parameters
- Execute routing decisions without human approval
- Automatically update blockchain records
- Self-optimize based on performance data
Quantum-Resistant Blockchain
As quantum computing advances, current blockchain encryption methods face potential vulnerabilities. The industry is already developing quantum-resistant algorithms to future-proof supply chain infrastructure.
Digital Twins at Scale
Every physical product will have a digital twin on the blockchain, updated in real-time by IoT sensors. AI will simulate entire supply chain networks in digital space, allowing companies to test scenarios before implementing changes, similar to using AI for business optimization.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
Industry consortia will evolve into DAOs where governance decisions are made collectively through smart contracts and token-based voting. This solves the “TradeLens Trap” by ensuring no single player controls the network.
Why Partner with Iterators
We’ve been building enterprise software for over 10 years, with specific expertise in:
AI and Machine Learning: Our team has deployed production ML systems processing millions of predictions daily. We understand the difference between research models and production-grade AI.
Blockchain Development: We’ve built systems on Hyperledger Fabric, Ethereum, and custom blockchain implementations. We know when to use public vs. private chains, similar to our blockchain applications expertise.
Enterprise Integration: We’ve integrated AI-blockchain solutions with SAP, Oracle, and custom ERP systems. We understand the reality of legacy infrastructure.
Industry-Specific Experience: We’ve worked with clients in fintech, supply chain, e-commerce, and healthcare. We bring domain knowledge, not just technical skills.
Proven Process: Our development methodology combines agile practices with the rigor required for enterprise deployments. We deliver working software, not just documentation.

Schedule a consultation to discuss your specific supply chain challenges and how AI blockchain integration for supply chain can solve them.
FAQ: AI Blockchain Integration for Supply Chain
What is AI blockchain integration for supply chain?
AI blockchain integration for supply chain combines the immutable, decentralized data layer of blockchain with the predictive and analytical capabilities of artificial intelligence. Blockchain ensures data integrity and trust, while AI extracts insights and enables autonomous decision-making for logistics operations.
Which industries benefit most?
Industries with complex, multi-party supply chains benefit most: food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, automotive, luxury goods, electronics, and aerospace. Any industry where traceability, authenticity, and real-time visibility create competitive advantage can leverage this technology.
How much does implementation cost?
Costs vary widely based on scope:
- Pilot project: $50,000 – $150,000
- Production deployment: $250,000 – $1,000,000+
- Enterprise-wide implementation: $1,000,000+
However, with average annual disruption costs of $184 million, the ROI calculation often justifies the investment within 12-18 months.
How long does implementation take?
Typical timeline:
- Pilot: 3-6 months
- Production deployment: 6-12 months
- Full ecosystem maturity: 18-24 months
The key is starting with a focused pilot that proves value quickly.
Is blockchain secure for supply chain data?
Yes, when implemented properly. Blockchain’s cryptographic security is extremely robust. The security considerations are:
- Use permissioned blockchains (Hyperledger Fabric) for sensitive data
- Implement proper key management
- Use Zero-Knowledge Proofs for privacy-preserving verification
- Regular security audits of smart contracts
Can it work with existing ERP systems?
Absolutely. Modern AI blockchain integration for supply chain implementations use middleware layers and APIs to integrate with legacy systems. You don’t need to replace your ERP—you augment it with blockchain for trust and AI for intelligence.
What’s the difference between using AI or blockchain alone?
AI alone: Provides predictions but depends on data quality you can’t verify. Vulnerable to “garbage in, garbage out.”
Blockchain alone: Provides trust and traceability but can’t predict or optimize. It’s a ledger, not a brain.
AI + Blockchain: Blockchain ensures the data AI uses is trustworthy and immutable. AI provides the intelligence to act on that trusted data. The combination creates autonomous, self-optimizing supply chains.
Conclusion: The Cognitive Supply Chain Imperative
The “permacrisis” of the 2020s has ended the era of static supply chain management. The future belongs to Cognitive Supply Chains—networks that think, predict, and adapt through AI blockchain integration for supply chain operations.
This transformation requires the symbiotic integration of AI and blockchain: one to provide the truth, the other to act on it. According to Harvard Business Review research on transparent supply chains, this transparency is no longer optional—it’s essential for survival.
For technical leaders, the path forward is clear but challenging. It requires moving beyond cryptocurrency hype and AI buzzwords to focus on rigorous engineering:
- Defining data standards
- Architecting permissioned ledgers
- Deploying robust oracle networks
- Building ML models on trusted data
The costs of implementation are significant, but the costs of inaction—measured in hundreds of millions of dollars in annual disruption losses—are far greater.
The question isn’t whether to implement AI blockchain integration for supply chain. The question is whether you’ll lead this transformation or scramble to catch up when your competitors already have cognitive supply chains and you’re still operating blind.
Ready to build your cognitive supply chain? Contact Iterators today. We’ll help you navigate the technical complexity and deliver working systems that provide competitive advantage, not just proof-of-concept demos.
The Suez Canal won’t be the last crisis. The companies that survive the next one will be those that can see it coming and autonomously adapt. Will you be one of them?
